NUCLEAR POWER, WHAT IS IT? AND HOW CAN IT HELP US DEFEAT CLIMATE CHANGE.
- Tomas Jacinto
- Feb 6, 2022
- 3 min read
Nuclear Power can help us defeat climate change. But how? To understand this, we must first understand the process of generating energy through nuclear power. Using nuclear power to produce electrical voltage is similar to using other types of energy sources. Inside the nuclear reactor there is normally Uranium isotopes. Inside the core when a neutron is shot into a nucleus of uranium isotopes, as it joins the nucleus, the residual strong nuclear force (force “holding” the neutrons and protons together) disappears completely. Meaning that coulomb force is the only force acting on the nuclei of uranium. Therefore, as the coulomb force is the only force acting on the nuclei, the isotope breaks up and, in this process, generates a lot of energy. To control the nuclear chain reactions control rods are used. These control rods are made of elements that do not react with the Uranium isotopes. They are then inserted into the reactor so that it blocks more reactions from happening. Moreover, the energy then generated through this process heats up tubes made up of conductive metals, which have water flowing through them. The boiled water then becomes steam at a very high pressure, the steam made is passed through a turbine. Since the steam is very high pressure, the steam makes the turbine spin very quickly, the turbine is connected to a generator that then converts kinetic energy into voltage. That’s how you generate electrical energy with nuclear power.

Since no fossil fuels are used, nuclear power does not have any CO2 emissions. As we know climate change is a global issue that has been a problem for many years but the setback with our current energy generation is that we use coal and other fossil fuels to generate energy. Nuclear power generates as much energy as fossil fuels without producing any greenhouse gas emissions. The energy generated by nuclear releases as many emissions as renewable energy. Therefore, when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing, nuclear power is a consistent method of generating energy without producing greenhouse gases.
Although nuclear does not release greenhouse gases it does still produce hazardous waste. Radioactive waste stays activate for tens of thousands of years. After the core does not produce enough energy to make profits for the energy company, they shut down the reactor. The problem is that the core, the concrete and metals exposed to radiation will still stay radioactive, it has to be well protected from any type of life or such will be infected to radioactivity, which, can produce very negative effects such as cancer. In addition, Japan has unfortunately approved releasing wastewater into the ocean. Although the water will be diluted in order for the radiation levels to be those set for drinking water the local fishing industry has strongly opposed as have China and South Korea. Furthermore, the radioactive material has to be safely guarded as this waste can still be used to make nuclear bombs.
Another factor to take into account when looking at different energy sources is the number of deaths per terawatt of energy generated. (see table below)
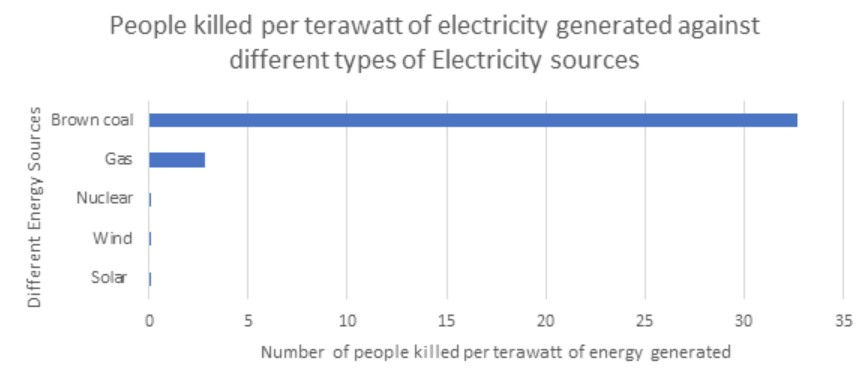
The graph shows brown coal kills around 32.7 people per terawatt, gas kills around 2.8, nuclear wind and solar combined kill less than 0.15 people per terawatt per year.
However, nuclear reactor disasters do happen and a factor to how safe the energy is. As we know nuclear reactors come with a risk as they are highly radioactive, in addition nuclear reactors are close to rivers and coasts for cooling purposes thereby making these vulnerable to tsunamis and natural disasters. In 2010 a tsunami hit three nuclear reactors near the coast of Japan. The reactors themselves were not harmed but the tubes that brought the cooling were damaged and since there was no cooling the reactors went into meltdown, and because of this they melted through the concrete and radiation started leaking. Therefore, Japan had to create a 20-kilometre exclusion zone so that no one would be harmed due to radiation. Furthermore, we all know of the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 when overheated uranium melted protective barriers, 2 people were killed immediately, 28 died later on. Scientists predict that the total death toll because of exposure to radiation will be in the thousands.
In conclusion, I believe that we will need nuclear power in order to reach a sustainable future. As we saw throughout this article nuclear power is clean and also safe. However nuclear reactors disasters are a factor in safety. Overall, I believe that it is a good energy source and necessary if we are trying to reach net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
Tomás Jacinto




Comments